Laminated Films for Packaging and Insulation
Laminated films made of plastic, paper, and aluminum are used in a variety of application areas. In the packaging industry, laminated films are found in the food sector as well as in industry or pharmacy. Plastic, paper, and aluminum films are also found in construction and other sectors. AlFiPa is your specialist for all types of laminated films. With over 40 years of industry experience, we develop laminated films that are precisely tailored to your needs.
What are laminated films?
Laminated films are multi-layer films that are made by combining different materials (e.g., aluminum, plastics, or paper) together. These films consist of two or more layers of different materials that are laminated or coated together.
The combination of different material properties allows for the benefits of individual layers to be utilized. The selection of materials depends on the desired properties, such as barrier properties against oxygen or water vapor (moisture), or light. Mechanical properties like tear resistance, elongation, or thermal resistance also play a role.

Aluminum laminated film is a key element in the packaging industry that significantly improves the longevity and freshness of products. These films consist of a thin layer of aluminum laminated between other materials, such as plastics or paper, to combine the benefits of different materials in a single packaging solution. The aluminum layer provides an excellent barrier against light, oxygen, moisture and bacteria, making it ideal for packaging food, beverages, pharmaceuticals and cosmetic products.
-
Aluminum / plastic combinations
Aluminum / plastic combinations as composite films have become indispensable in the processing, pharmaceutical and food industries, but also in many other sectors. AlFiPa has clearly positioned itself here and has made a name for itself throughout Europe as a reliable partner. -
Duplex- und Triplexfolien
AlFiPa supplies duplex and triplex films for technical applications and industries. Composite films can be provided with an additional barrier layer in the sealing film. In many cases, the film is embedded in PE or EVOH. Two-layer laminated films are referred to as duplex. Composite films made of 3 layers are called triplex. -
Typical areas of application for laminated films
Typical areas of application are those in which composite film types are used functionally, for example with additional barrier layers. Properties such as high mechanical strength, resistance to cold and heat, but also the permeability of water vapor, are properties that are largely determined by the structure and composition of the film layers of a composite film. AlFiPa customers have the advantage of receiving a composite film type tailored to their needs.
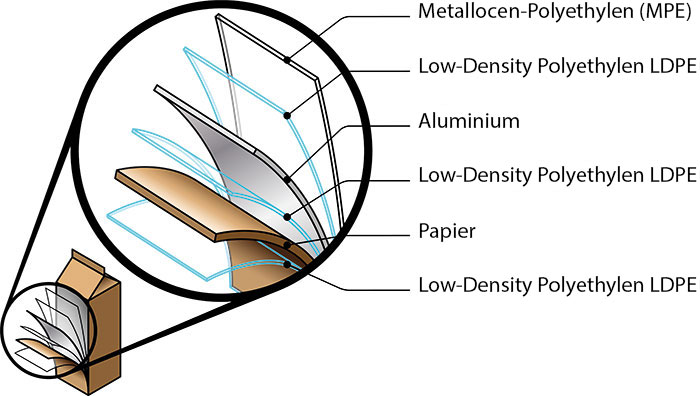
Composite film composition example
What are laminated films made of?
Laminated films are composed of a variety of materials, often selected for their specific properties to suit different applications. Here’s an overview of the common materials used in laminated films:
- Polyethylene (PE):A thermoplastic polymer known for its flexibility and barrier properties. It can be used in various thicknesses, and with different additives, it can achieve specific protective or barrier properties.
- Polypropylene (PP):Another thermoplastic polymer, valued for its excellent mechanical properties. It’s often used for its strength and heat resistance.
- Polyester (PET):PET is known for its high transparency, strength, and chemical resistance. It’s frequently used in packaging for food and beverages due to its good tear resistance and is also used in insulation films for construction.
- Polyamide (PA):Known for its tremendous tear strength and toughness, making laminated films especially durable when used. PA is generally more tear-resistant than PET and is used, for example, in the packaging of frozen food.
- Aluminum Foil:Aluminum provides an excellent, lasting barrier against oxygen, light, and moisture. It’s used in food packaging to extend shelf life.
- Metalized Films:These films are increasingly covering a broader spectrum of applications. The barrier is not as high as that of “real” aluminum but is sufficient for most cases, especially for flexible packaging when the products only need to be preserved for a limited time. Metalized films are used, for example, in packaging for fast-moving consumer goods. There are also special applications for metalized films in insulation, especially when a 100% barrier is explicitly not desired.
- Reinforcements like Fabrics and Non-Wovens:Fabrics and non-wovens increase tear resistance and, in particular, tear propagation resistance: if such a laminated film is torn, the tearing stops at the next thread of the fabric or non-woven. These can be made from various materials, including fiberglass, PET, PP, or PE, and are primarily used in industrial films and insulation. However, they are less suitable for consumer packaging due to the surface texture they impart, and they would also prevent the packaging from being easily torn open by hand.
- Paper: Considered an environmentally friendly material, especially when recycled, paper can also provide a premium tactile experience. It’s used in laminated films for both packaging and insulation. Due to its cost-effectiveness, paper is often used in insulation to reduce costs.
In addition to these typical materials, numerous other types of films can be used in the production of laminated films, including copper, stainless steel, and a variety of other plastics.

Composite foil is increasingly being used as an innovative insulation material in the construction industry to ensure efficient thermal and acoustic insulation in buildings. Due to its multi-layered nature, it effectively blocks heat exchange and reduces noise, resulting in improved living comfort and energy savings. The flexibility and ease of installation of composite foil make it a preferred choice for sustainable building projects and renovations that demand the highest standards of environmental friendliness and energy efficiency.
Manufacturing process for laminated films
The production of laminated films typically involves two main processes: laminating (also known as laminating) and coating (extruding). Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the film and its intended application.
Lamination
Lamination, also called laminating, involves bonding two or more film webs together with an adhesive. Laminating can be done through various methods:
- Dry Laminating: In dry laminating, an adhesive dissolved in water or solvent is applied to one of the film layers and then pre-dried in a drying tunnel. Through heat and pressure, the adhesive is re-melted, and the film is bonded to a second web.
- Wet Laminating: In wet laminating, a viscous adhesive is applied to one of the films. Unlike dry laminating, the adhesive is still wet when bonding the two webs together. The second web is pressed onto the wet adhesive, and the solvent evaporates under pressure and heat.
- Solvent-Free Laminating: Solvent-free adhesives usually consist of two components. When these two components come together, a chemical reaction occurs, creating the adhesive force. Since no solvents need to escape, no drying is necessary.
- Wax Laminating: In this method, the adhesive consists of melted wax or hot melt, which is applied to the carrier materials. This process is often used for laminating paper+paper or paper+aluminum combinations.
Extrusion
Extrusion is an alternative manufacturing process for laminated films, also referred to as the “coating process” or “extrusion coating.” This method involves using liquid polymer material, such as PE or PP, which is sprayed in liquid form onto the carrier material and then dries to form a film.
Both laminating and extrusion techniques allow for the production of laminated films with specific properties, including barrier effects, mechanical strength, and thermal resistance, tailored to a wide range of applications in packaging, construction, and other industries.
-
Laminating (also known as laminating)
Laminating (also known as laminating) is a process in which at least two film webs are bonded together. In the full-surface process, where the individual layers are connected, a composite material consisting of several individual layers is created. A wide variety of materials can be bonded together in this process. In addition to the most common composite materials in films, such as plastic and aluminum, cardboard or textiles, for example, are also fundamentally suitable. -
Adhesive / Binding agent
Adhesives / Binding agents. Suitable adhesives in industrial production include varnishes, glues, and even waxes. Laminating is often used for decoration or to improve material properties. Adhesives are applied to the so-called carrier web, which then absorbs the adhesives. In the duplex process, the second film web is pressed against the carrier web, creating a two-layer laminate. Film web laminations are carried out to achieve desired optical properties and to influence the barrier function of the carrier material.
The choice of web laminating method depends on the product’s application. AlFiPa provides customers with a crucial planning advantage early on, during the initial and planning phases of product packaging. We collaborate with you from the idea to the finished product, tailored precisely to your company.
Within our company, we have a variety of application methods and techniques for your industry. Whether from the food or non-food sector, construction industry, pharmaceutical, or medical technology field. Laminated films from AlFiPa give you a technological edge through innovative technology.
Lamination can be carried out using various methods:
-
Wet laminating
In this process, to bond film webs together, the laminating or binding agent is applied wet. This application is very common when laminating papers with aluminum. The result is an aluminum/paper laminate in which both materials have formed an inseparable bond. -
Dry laminating
Here, adhesive is used as the binding agent, which has been dissolved in water or solvent and applied to one of the film webs. The actual lamination occurs when one film web is pressed against the other film web under high pressure by rollers. The pressure must be applied in such a way that an optimal bond between both webs is ensured. -
Wax lamination
In this process, the adhesive, here wax or “hot melt,” is applied in its melted state to one of the two substrate materials. This method is used for the production of paper or paper-aluminum foil laminations, which are often used for packaging cookies and baked goods. As the binding agent, the glue is replaced by wax in this case. -
Solvent-based lamination
In laminating, solvents are used for the adhesives that ensure good solubility of the glue but should be avoided, for example, in films used for food products to meet strict regulations. Therefore, the process is distinguished between solvent-based and solvent-free. -
Solvent-free laminating
Solvent-Free Laminating. In this process, solvents are completely avoided. Adhesives that do not contain solvents are based on a two-component system; they react with each other and do not require a drying phase.
Coating (extruding)
In the coating process on a substrate material, coating material is applied to the moving web of substrate. Flexible webs of substrate are essentially unrolled and coated in this manner. The result is a substrate material, which can be films, papers, or aluminum foils, that possesses new properties following this functional or optical finishing. AlFiPa produces films according to the desires of the processing industry, serving as the base material for, for example, new packaging or insulation materials.
-
Coating types
Varnishing is the most common type of coating that can produce a high-gloss surface. In the food industry, certain processes are customary for specific foods. For example, certain barrier protection functions are required for films used as the base material of food packaging. As a company, we can produce films that, for example, protect and seal flavors. -
Coating systems
Coatings are applied within a printing machine or on coating and laminating equipment. Special types of coatings are applied to films but can also be applied to labels, release papers, or laminates. The range of applications spans from industrial to medical uses.
In coating equipment or so-called coating lines, the common technique involves application via rollers. Before flexible materials/film webs are wound on rolls, they pass through a drying tunnel.
The composite films are available in the following widths:
- 8-10 mm (on request)
- 10-50 mm
- 50-100 mm
- 100-200 mm
- 200-300 mm
- 300-400 mm
- 400-500 mm
- 500-750 mm
- 750-1000 mm
- 1000-1300 mm
- 1300-1600 mm
- 1600-1900 mm
- 1900-2100 mm
- from 2100 mm (on request)
Typical types of our laminated films
The specially multi-layered material is suitable for packaging bags and, for example, packaging that must be suitable for pasteurization or should have special thermal properties. Aluminum creates a strong barrier effect. AlFiPa, as a supplier with now 40 years of experience, can provide the processing industry with material that can be printed with up to 10 different high-gloss colors. Typical packaging solutions are found, for example, in coffee or sauce packaging.
Combinations from the AlFiPa program: The material combination from which the laminated film is made determines its functional use. Here are the common basic material combinations in laminated films:
| Material combination | Areas of application | Surface suitability |
|---|---|---|
| PET+Alu+PE | Packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| PET+Alu+PP | Packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| PET met + PE | Packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| PP met + PP | Packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| PP+Alu+PP | Cables | printable |
| PET+Alu+HDPE | Bulk packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| Papier+Alu+PE | Packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| Papier+PE | Packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| Alu+PE | Insulation | also with protective coatings |
| Alu+PET | Insulation | also with protective coatings |
| PET+Alu+PET | Cables, insulation | printable |
Table 1: Basic material combinations for laminated films
Composite films with scrim and fabric:
Insulation manufacturers across Europe rely on aluminum and composite films from AlFiPa. In this form, insulation materials are created that effectively provide thermal and acoustic insulation.
One of our core competencies lies in the customer-specific provision of materials that are demanded in the processing industry.
| Material combination | Areas of application | Surface suitability |
|---|---|---|
| PET+Clutch+Alu+PE | Insulation, bulk packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| PET+Clutch+Alu+PEТ | Insulation, bulk packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| PET+Alu+Fabric | Insulation, bulk packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
| PETmet+Clutch | Insulation, bulk packaging | printable with up to 10 colors |
Table 2: Laminated Films with Fabrics and Non-Wovens
In addition to these typical material configurations, we offer a wide range of structures and specifications tailored to your specific wishes and needs. We are happy to advise you on which laminated film is best suited for your requirements – even for small and medium quantities. 40 years of expertise in this field make us a reliable partner – starting from the early phase of product development.
Properties of Materials Used in Laminated Films
Polyamide (PA) laminated films are characterized by high strength under mechanical stress. This type of film has very good barrier properties, which decrease with increasing humidity. Weather resistance, cold and heat resistance, as well as insensitivity to water, are typical properties of this film. This type of laminated film can be easily thermoformed and is stretchable.
| Foils | Features |
|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Composite films based on polyethylene have optimum properties in terms of barrier function, transparency, thermoformability, rigidity and toughness. This thermoplastic material is ideal for the production of packaging. |
| Polypropylen (PP) | This type of film is characterized by its high mechanical strength. Polypropylene composite films do not require an additional barrier layer as they are permeable to oxygen. They are insensitive to water and form a very good water vapor barrier. Polypropylene-based films are only partially heat-resistant. |
| Polyvinylchlorid (PVC) | PVC composite film types are characterized by very high rigidity and good thermoformability. However, this type of film has a low resistance to heat and cold. |
| Cellophane | This component of the composite film has a good barrier function at low humidity, but low mechanical strength and is not weatherproof. |
| Polyester (oPET) | Composite films containing polyester are resistant to mechanical stress, heat and cold and are also insensitive to water. Polyester-based films have good barrier properties and can be equipped with additional barrier layers. |
We offer laminated films for the following applications:
Food and Pharmaceutical Packaging
Laminated films are the first choice for food and pharmaceutical packaging. The structure of AlFiPa laminated films is tailored to the necessary functions of future food or pharmaceutical packaging. Here, protective functions are crucial in preserving product properties, but other functional properties are also considered from the outset when choosing the type of film.
These can include features such as opening behavior, resealability, as well as optical properties that can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Marketing-oriented properties, such as surface texture, provide an advantage at the point of sale (POS). To realize these complex properties in films, we differentiate between layer components and film types that embody the desired properties. We offer the processing industry the opportunity to make a preliminary selection to assign product properties to the film that will functionally and visually become the base material for packaging.

Aluminum composite film plays a central role in the food industry by providing an unsurpassed barrier against light, moisture and oxygen, extending the shelf life and freshness of food. Its ability to preserve flavors and qualities of the contents makes it the ideal choice for packaging a variety of products, from snacks to freeze-dried foods. In addition, aluminum composite film enables efficient storage and distribution, making it an indispensable part of modern food packaging solutions.
Construction and Industry
In addition to the processing industry, with its ever-new requirements for packaging, the construction sector has evolved into an area where films, as carriers for insulation materials, are becoming increasingly important. Modern laminated films used as carrier webs for mineral wool or other insulation materials are equipped with numerous functions.
-
Prevent heat loss
Most of the heat is transferred via radiation, i.e. houses without insulation lose heat in this way. Energy is lost via roof surfaces in particular.Aluminum and aluminum composite foils can be functionally structured in such a way that they can reflect up to 96 percent of heat loss via radiant heat. These properties make composite foils in particular an ideal carrier material for insulating materials on roofs or house walls. It is also easy to shape and adapt.
-
Heat reflection & vapor barrier in one
Composite foils as a carrier material for insulation materials and mineral wool combine the thermal properties in the insulation, but also act as a vapor barrier that prevents mold growth within the intermediate layers of the insulation. -
Insulation
Pure aluminum foils are being replaced by aluminum composite foils, especially in the area of insulation. Plastic foil is laminated with aluminum foil, either in one layer or in several layers. Common plastic films are also made of PET, PP or PE. -
High tear resistance & optimal processing
On the one hand, composite films are more tear-resistant and can be better bonded to insulating materials. If you want to integrate additional functional features into the laminated film, additional scrims are possible, which can also be laminated into the film.Perforated aluminum foil as a composite foil enables optimum air circulation. Perforated foils have established themselves as an insulating material, which on the one hand insulate well thermally, but on the other hand allow air circulation through the perforation with micro-holes. This is always very important when large thermal fluctuations can cause condensation to form on the inside and outside of the insulation.
A vapor barrier is required in the basement area of houses. Here, film types without perforation but with thermal insulation are available as insulation material.
Laboratory Applications. Laboratory Films – Laminated Films
AlFiPa laminated films are used in physical, chemical, and biological laboratories across Europe and the world. One application is the sealing of containers, such as measuring flasks and jars. In these instances, films are often used as a functional closure for measuring flasks and technical glassware. AlFiPa has once again positioned itself as a partner in science and research, offering laminated films as roll stock in various thicknesses, even in small quantities. Customizations are possible upon customer request.
Further Processing and Finishing Techniques for Laminated Films According to Customer Specifications
We supply companies in the B2B sector at the highest quality level. We have production and storage facilities that enable short paths and allow us to respond to smaller orders and small quantities. We are experts in the field of functionally and visually enhanced laminated films.

Composite films are increasingly used in insulation due to their excellent insulating properties, where they help to increase energy efficiency through improved thermal and acoustic insulation. Their multi-layer composition, which often includes reflective metal layers and thermoplastic materials, makes it possible to maintain a constant temperature and minimize noise pollution in both residential and commercial buildings. This flexibility and efficiency make composite foil a cost-effective solution for environmentally friendly construction and renovation projects.
Printing, Varnishing, Perforating
We work with all common printing techniques, offering our customers the best print quality on types of laminated films. In addition to printing, we realize almost every functional and optical finishing on laminated films, such as perforating and varnishing.
The specific processes are: Gravure printing (rotogravure), flexographic printing, screen printing, offset printing, digital printing
-
Flexodruck
The flexographic printing process uses flexible printing plates that absorb ink via an ink roller. The raised areas of the so-called clichés (printing plates) are then imaged on the film. The print is applied to the film via a cylinder roller. -
Tiefdruck – Rotogravur
The gravure printing process (rotogravure) is one of the most versatile processes, particularly in the production of films and packaging. It offers the widest range of applications with optimum printing properties on film surfaces. In rotogravure, the areas on which the print is to be applied are prepared by engraving or etching the area so that the print can be applied. The areas that are to be print-free are removed with a doctor blade. The advantage of gravure printing: Prints can be realized on foils that have photo quality. -
Offsetdruck
Offset printing is a flat printing process in which the areas on which the print is to be made are raised. Areas that are not raised are not printed. The printed image is applied using a rubber blanket. -
Digitaldruck
Similar to traditional paper printing, digital printing has established itself as the more economical printing method, even for foil printing. Unlike paper printing, however, the application of ink to film is more complex and film must be prepared for the application of ink. Digital printing is the more cost-effective process, especially for large print runs. The solvent printing process is used for printing on film.
Delivery of small quantities
“Not everything is possible, but we make the possible happen!”
Can’t find a supplier for smaller quantities? Would you like to sample or do you have fluctuations in the quantities required?
Custom-made products. Do you need material in different dimensions that is customized for you or laminates as duplex or triplex in small quantities? Here, too, we always have suggestions for solutions.
Custom Converting to Small Rolls According to Your Requirements
While large orders are naturally pleasing to us, what happens on the other hand when small quantities or special solutions are needed? We must also provide solutions for our customers in these situations, and we do. Here too, we give our customers the AlFiPa promise: We process films in the manner and quantities needed.
Sampling
We have a large collection of different materials in various thicknesses for hand samples, so you can see and feel the material. Especially in the area of sampling, we are happy to provide you with suitable samples or packaging solutions. At AlFiPa, we have an extensive collection from 40 years of company history. We are pleased to provide you with suitable samples.
Our Production, Standards, and Quality Assurance
As a supplier of laminated films, we are accustomed to handling flexible materials. We are inflexible in our quality standards, which are particularly important in the area of functional laminated films. Imagine, for instance, a laboratory where measurements are distorted due to faulty laminated film sealing the flasks. Unthinkable for us! Constant checks, both internally and through external testing laboratories, guarantee the quality of laminated films our customers can expect.
We conduct extensive material tests that check for puncture resistance, seal seam strength, coefficient of friction, or, for example, tensile strength of laminated films. Additionally, targeted testing of the functional properties of laminated films, such as the function of the vapor barrier, is regularly conducted.
We will be happy to answer any questions you may have about laminated films. Contact one of our department experts




